Standard Toilet Dimensions
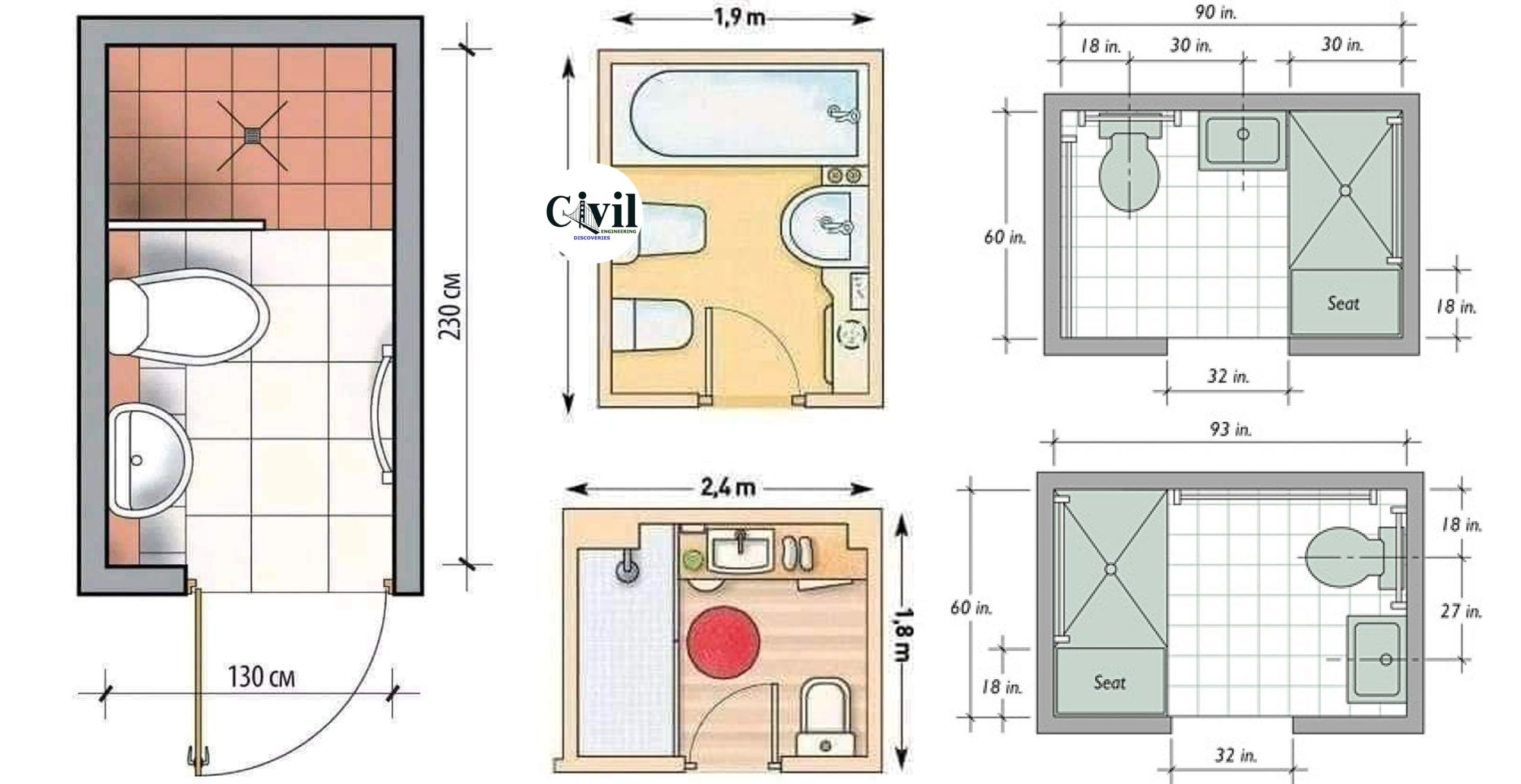
Understanding the standard dimensions of toilets is crucial for planning bathroom renovations or selecting new fixtures. While there are variations depending on the type and model, a general understanding of the typical sizes can help ensure a comfortable and functional bathroom.
Standard Toilet Dimensions in Meters
The table below presents the standard dimensions of toilets in meters, encompassing length, width, and height:
| Toilet Type | Length (m) | Width (m) | Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| One-Piece Toilet | 0.66 – 0.76 | 0.38 – 0.41 | 0.76 – 0.81 |
| Two-Piece Toilet | 0.61 – 0.71 | 0.38 – 0.41 | 0.76 – 0.81 |
| Wall-Mounted Toilet | 0.51 – 0.61 | 0.38 – 0.41 | 0.36 – 0.41 |
Differences in Dimensions Between Common Toilet Types
One-piece toilets, known for their sleek design, typically have a slightly longer length compared to two-piece toilets. This difference arises from the integrated tank and bowl design in one-piece toilets. Two-piece toilets, with their separate tank and bowl, generally offer more flexibility in installation and maintenance. Wall-mounted toilets, characterized by their space-saving design, are significantly shorter in height due to the concealed tank behind the wall.
Impact of Bowl Shapes on Overall Toilet Dimensions
Toilet bowl shapes, such as elongated and round, also influence overall dimensions. Elongated bowls, offering a more comfortable seating experience, are generally longer than round bowls. The extended length of elongated bowls translates to a greater overall toilet length.
Factors Influencing Toilet Dimensions
Several factors contribute to variations in toilet dimensions, including:
- Age of the Toilet: Older toilets often have different dimensions compared to modern models. Advancements in design and technology have led to more compact and efficient toilet designs.
- Manufacturer: Different manufacturers may have their own design standards and specifications, resulting in varying dimensions across models.
- Specific Model: Even within the same manufacturer, different models can have distinct dimensions. This variation reflects the design choices and features incorporated into each model.
Standard Bathroom Dimensions

A standard bathroom’s size can vary depending on its intended use and the overall size of the house. However, there are some common dimensions that are generally considered to be suitable for a comfortable and functional bathroom. This section explores the typical dimensions of a bathroom, taking into account different layouts and their impact on space and functionality.
Typical Bathroom Dimensions, Standard size of toilet and bathroom in meters
The table below Artikels the standard dimensions of a bathroom in meters, including the size of the toilet area, shower/bathtub area, vanity area, and other essential elements.
| Element | Dimensions (in meters) | Toilet Area | 0.9 x 1.2 | Shower/Bathtub Area | 1.2 x 1.8 | Vanity Area | 0.9 x 1.5 | Other Essential Elements | 0.6 x 1.2 | Total Area | 3.6 x 4.5 |
|---|
The total area of a standard bathroom is generally around 16.2 square meters. However, this can vary depending on the size of the house and the number of bathrooms.
Bathroom Layouts and Their Impact on Space Requirements
Different bathroom layouts have different space requirements and impact the overall functionality of the bathroom. Here are some examples of common bathroom layouts:
- Single-Sink Bathroom: This layout typically features a single sink, toilet, and shower/bathtub. It is the most common type of bathroom layout and is suitable for small to medium-sized bathrooms.
- Double-Sink Bathroom: This layout features two sinks, a toilet, and a shower/bathtub. It is ideal for larger bathrooms and provides more space for storage and amenities.
- Walk-in Shower Bathroom: This layout features a walk-in shower, a toilet, and a vanity area. It is becoming increasingly popular as it provides a more accessible and modern look.
Visual Representation of a Standard Bathroom Layout
The following is a visual representation of a standard bathroom layout with dimensions clearly labeled:
[Description of the visual representation of a standard bathroom layout with dimensions clearly labeled. Include a description of the toilet area, shower/bathtub area, vanity area, and other essential elements. Provide details about the layout and the dimensions of each element. This is a placeholder for a detailed description of the visual representation.]
Different bathroom layouts have different space requirements and impact the overall functionality of the bathroom. For example, a single-sink bathroom will require less space than a double-sink bathroom. Similarly, a walk-in shower bathroom will require more space than a standard shower/bathtub bathroom.
Factors Influencing Bathroom and Toilet Size: Standard Size Of Toilet And Bathroom In Meters
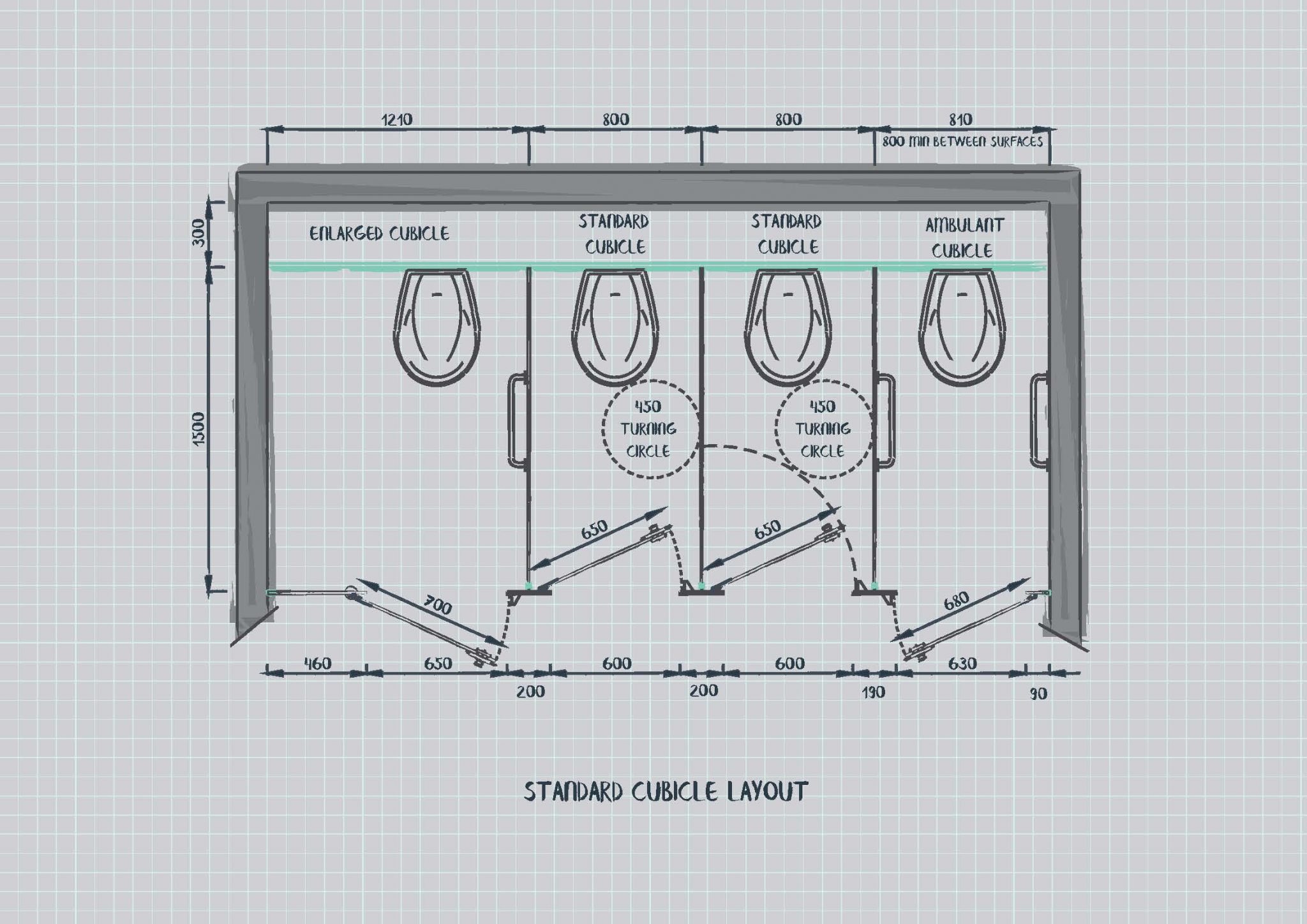
The dimensions of a bathroom and the size of a toilet are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, ranging from legal requirements to personal preferences. These factors determine the overall functionality, accessibility, and aesthetic appeal of the space.
Building Codes and Regulations
Building codes and regulations play a crucial role in establishing minimum bathroom and toilet dimensions. These regulations are designed to ensure public safety, health, and accessibility.
- Minimum Area: Building codes typically specify minimum square footage requirements for bathrooms, ensuring adequate space for fixtures and movement. For example, the International Residential Code (IRC) requires a minimum of 30 square feet for a bathroom with a toilet, sink, and tub or shower.
- Fixture Placement: Codes also dictate the minimum distances between fixtures, such as the toilet and the sink, to allow for comfortable use. These distances ensure sufficient clearance for maneuvering and accessibility.
- Accessibility Requirements: Building codes often incorporate accessibility requirements for bathrooms, particularly for people with disabilities. These requirements include provisions for wheelchair access, grab bars, and adequate maneuvering space.
Accessibility Requirements
Accessibility requirements significantly influence bathroom and toilet dimensions. These requirements ensure that bathrooms are usable and safe for people with disabilities.
- Wheelchair Access: Bathrooms designed for wheelchair users must have a minimum width of 36 inches for maneuvering, a turning radius of 60 inches, and clear floor space around the toilet.
- Grab Bars: Grab bars provide support and stability for users, especially when entering and exiting the shower or using the toilet. Building codes specify the location, size, and strength of grab bars for accessibility.
- Toilet Height: Accessible toilets are typically raised to 17-19 inches from the floor, allowing for easier transfer from a wheelchair.
Personal Preferences and Lifestyle Choices
Beyond building codes, personal preferences and lifestyle choices significantly influence bathroom and toilet size decisions.
- Family Size and Composition: Larger families often require larger bathrooms to accommodate multiple users simultaneously. Families with young children may prefer a wider toilet for easier access and a larger bathroom for storage and changing areas.
- Storage Needs: Individuals with extensive toiletries or bathroom accessories may require larger bathrooms with ample storage space for towels, toiletries, and other items.
- Aesthetic Preferences: Personal taste and design preferences influence bathroom and toilet size. Some individuals may prefer spacious bathrooms with large, luxurious fixtures, while others may opt for smaller, more minimalist designs.
